The AppData folder is an important part of Windows 10 and 11, storing essential data like settings, logs, and cache for your applications. Unlike the Program Files folder that stores installation files, AppData is more like a directory where persistent app-specific information is kept. Understanding what AppData is and how to manage it can help you keep your computer running smoothly.
What is the AppData Folder in Windows?
The AppData folder is a hidden directory in Windows where programs store their important data. This data can include app settings, caches, and logs. It is divided into three subfolders:
- Local: Stores data specific to a single device, such as cache files.
- LocalLow: Stores less critical data with limited system access, often used by browsers and certain apps.
- Roaming: Contains data that can sync across devices, often used for user profiles in enterprise environments.
These subfolders help Windows organize different types of app data effectively.
AppData vs. Program Files vs. Temp Folder
The AppData folder is different from other directories like Program Files and the Temp folder.
- Program Files: Stores core files needed to run programs, such as executables and libraries.
- Temp Folder: Contains temporary files that can be cleared after a session.
- AppData: Stores ongoing data for apps, allowing them to retain settings and logs between uses.
Over time, AppData can accumulate a large amount of data, especially if you have many applications installed. This is why it is important to know how to manage it.
How to Locate the AppData Folder in Windows 10 and 11
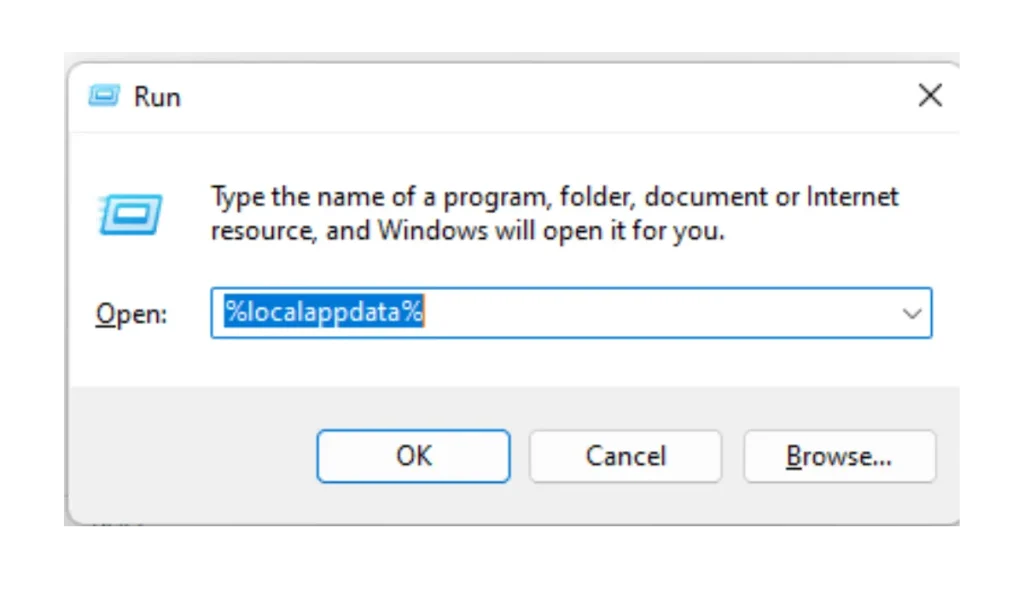
Finding the AppData folder is easy if you follow these steps:
- Press Windows + R to open the Run prompt.
- Type
%localappdata%and hit Enter. This will take you to the Local folder within AppData, which is often where large caches are stored. - You can also type
%appdata%in the Run prompt to access the Roaming folder, where data that syncs across devices is stored.
Tip: Remember that AppData is a hidden folder, so you need to enable viewing hidden items in File Explorer if you wish to navigate there manually.
Should You Delete Files from AppData?
Deleting files from AppData can be risky because some data is necessary for your apps to work properly. Here’s what you should know:
- Files You Can Delete:
- Cache files that are taking up space but not necessary for daily use.
- Logs that are not needed anymore.
- Files You Should Not Delete:
- Essential configuration files that apps need to operate.
Tip: If you’re not sure, only delete files from subfolders like Cache or Temp to avoid causing problems.
How to Safely Clean Up the AppData Folder
To safely clean up the AppData folder, you can try these methods:
- Manual Cleanup:
- Navigate to
%localappdata%or%appdata%and delete unnecessary cache and log files.
- Navigate to
- Third-Party Tools:
- Use trusted tools like CCleaner or Windows Storage Sense to automate the cleanup process.
These tools help identify files that are safe to delete, reducing the risk of accidentally removing something important.
FAQs About the AppData Folder
What happens if you delete the AppData folder?
Deleting the entire AppData folder can cause apps to malfunction or lose all settings. It’s best to only delete specific, non-critical files.
How to reduce the size of AppData safely?
Clear cache files and use disk cleanup tools to minimize the size without impacting functionality.
Conclusion
The AppData folder is important because it keeps your apps running smoothly by storing settings and logs. But it can grow a lot over time, so it’s good to clean it up regularly. Follow the steps in this guide to manage the AppData folder safely and keep your computer running well.
If this guide helped you understand and manage the AppData folder better, share it with your friends! Regularly taking care of your AppData can make your computer run faster, so spread the word.